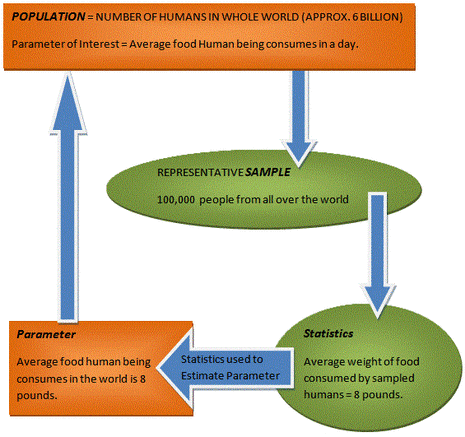
Population and Sample
Populations refers to the entire set of data or observations, the information of which we seek. It is impractical, if not impossible, to collect every single possible data point. Therefore, we choose to select some amount of data from the population (sample) and we assume that the properties of the sample is representative of the entire population. Therefore, one of the goal is to select representative sample so that sample statistics can adequately represent the population parameters.
In the above example, the population is all human beings living on the earth. It is impractical to collect information from 6 billion people on their daily food consumption. Therefore we chose a small subset of 100,000 people to collect the data (perhaps, because of limited budget or time - Remember: larger the sample, less is the error). The goal should be to obtain a representative sample. For example, if majority of people sampled are from North America then the statistics will not be representative of entire world population. (Most likely, the world average is lower than North America because higher percentage of people in under-developed nations suffer from malnutrition due to lack of food.) Therefore the sample should be collected from all over the world, for example, based on the percentage of world population in each continent.