Indoor Air
• Potential significant contributor to environmental risk.
• Component of green building design.
• Movement of air in an indoor environment:
-design of ventilation systems
-Natural ventilation systems
• Natural ventilation systems are best used in mild or moderate climates with minimal heating or cooling demands. Also in locations with minimal pollution. System capitalize on wind and thermally
generated pressures.
• Modern systems include heat exchangers to transfer energy in exhaust air to inlet air minimizing cooling and heating costs.
• Component of green building design.
• Movement of air in an indoor environment:
-design of ventilation systems
-Natural ventilation systems
• Natural ventilation systems are best used in mild or moderate climates with minimal heating or cooling demands. Also in locations with minimal pollution. System capitalize on wind and thermally
generated pressures.
• Modern systems include heat exchangers to transfer energy in exhaust air to inlet air minimizing cooling and heating costs.
Indoor Air Pollution
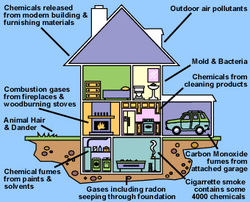
Indoor pollution sources that release gases or particles into the air are the primary cause of indoor air quality problems in homes. Inadequate ventilation can increase indoor pollutant levels by not bringing in enough outdoor air to dilute emissions from indoor sources and by not carrying indoor air pollutants out of the home. High temperature and humidity levels can also increase concentrations of some pollutants.
Understanding and controlling common pollutants indoors can help reduce the risk of indoor health concerns. Factors affecting Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) include ventilation rates and air exchange, the presence of pollutants from indoor sources (like volatile organic compounds, mold, and particulate matter), outdoor air quality, and building design and maintenance.
Important Factors and Equations Related to IAQ
Important Factors and Equations Related to IAQ
- Ventilation Rate: The rate at which indoor air is replaced with outdoor air. A commonly used metric is air changes per hour (ACH), which indicates how many times the air within a space is replaced in an hour.
Equation: ACH=Ventilation Rate (m3/h)Volume of the Room (m3)ACH=Volume of the Room (m3)Ventilation Rate (m3/h) - Dilution of Pollutants: Ventilation is used to dilute concentrations of indoor pollutants. The steady-state concentration of a pollutant can be estimated assuming perfect mixing and a constant emission rate.
Equation: Css=EQCss=QE Where CssCss is the steady-state concentration of the pollutant (mg/m³), EE is the emission rate of the pollutant (mg/h), and QQ is the ventilation rate (m³/h). - Indoor Air Pollutant Concentration from Outdoor Sources: The concentration of pollutants indoors not only depends on indoor sources but also on pollutants entering from the outdoor environment.
Equation: Cindoor=Coutdoor×(1−ER)+EindoorQCindoor=Coutdoor×(1−ER)+QEindoor Where CindoorCindoor is the indoor concentration, CoutdoorCoutdoor is the outdoor concentration, ERER is the efficiency of removal by the HVAC system or other means, EindoorEindoor is the indoor emission rate, and QQ is the ventilation rate. - Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Levels: CO2 levels are often used as an indicator of IAQ, particularly to assess ventilation effectiveness. While CO2 itself is not a pollutant at typical indoor concentrations, high levels indicate inadequate ventilation.
Equation for estimating outdoor air ventilation rate per person: Voa=(Cin−Cout)×QPVoa=P(Cin−Cout)×Q Where VoaVoa is the outdoor air ventilation rate per person (L/s per person), CinCin is the indoor CO2 concentration (ppm), CoutCout is the outdoor CO2 concentration (ppm), QQ is the total ventilation rate (L/s), and PP is the number of people.
